Asthma pathophysiology is the study of the changes that occur in the lungs related to asthma, changes like inflammation and bronchoconstriction. These conditions are examined in order to better understand the processes leading to asthma and many of its related complications.
The studies include everything that is thought to contribute to asthma. The consequences or results of these studies can be used as part of one’s treatment for the disease of asthma. The following topics are all generally considered to be part of asthma pathophysiology: allergies, common asthma triggers, the immune system, bronchoconstriction, inflammation and air passageway remodeling.
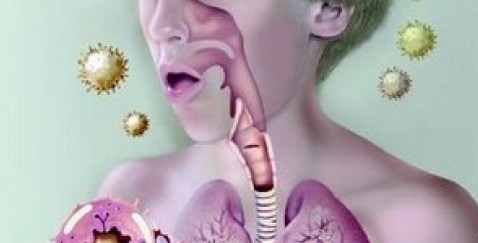
There are three asthma pathophysiology changes that happen in the lungs as one’s asthma symptoms become worse. As air passageways gradually become more inflamed and irritated, more mucus is produced, clogging the lung’s air passageways. Then the airways of the lungs are caused to swell due to the person’s asthma attack symptoms. Finally, the muscles of the person’s air passageways constrict in response to the asthma attack, meaning they become tighter and smaller.
To fight these symptoms, two main types of drug treatments used are bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications.
Bronchodilators offer rapid relief, freeing up the air passageways to allow for more air to flow to and from the person’s lungs. Bronchodilators are asthma medications made to relieve many of the asthma sufferer’s symptoms by allowing the muscle bands in the lungs that tighten around the person’s air passageways during an asthma attack to relax. Typically breathing will improve almost instantly for the patient. Similar to the anti-inflammatory medications, bronchodilators reduce mucus in the lungs.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are the most vital kind of asthma therapy for people suffering from the disease. With these medications, the asthma patient is able to attack asthma attacks on an on-going basis. Another important medication comes in the form of a steroid called corticosteroids. These anti-inflammatory drugs provide the lungs relief by reducing mucus production and swelling in the air passageways.
Most doctors and health care professionals will agree that the most effective and easiest treatment for a person’s asthma is to take control of the disease. This can be done in many ways, such as by researching everything available about it and initiating lifestyle changes and changes around the house which can significantly impact the frequency and severity of one’s asthma symptoms and attacks.
Some of the non-medicinal ways in which one can get a handle on the symptoms of asthma are avoiding asthma triggers like pet dander and dust mites and monitoring asthma symptoms by way of a daily diary.

In people whose asthma signs and symptoms tend to be comparatively more severe than those suffered by some others, long-term inflammation might progress into some permanent changes in their air passageways, which is referred to as airway remodeling. This is due to the fact that the actual structure of the air passageway walls can change and lead to blockage that cannot be completely reversed with treatment.
Understanding the pathophysiology of asthma will help a person understand how his or her asthma behaves and why it behaves that particular way. It will also lead the patient to discover what makes his or her symptoms better and what makes them worse. In this way, one can learn what one needs to do in order to harness his or her asthma and place it under his or her control.
