The National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP) lists five crucial areas an asthma medicine should be expected to do in order to effectively treat the symptoms of the disease. These are to control asthma, to prevent asthma symptoms, to enable the asthma sufferer to perform what are considered to be normal activities without incurring symptoms, decrease the number of asthma attacks and help the asthma sufferer use quick-relief medicines less frequently.
Most doctors and health care professionals will agree that the most effective and easiest treatment for a person’s asthma is to take control of the disease by researching everything available about it and initiating lifestyle changes and changes around the house which can significantly impact the frequency and severity of asthma symptoms and attacks.
Some of the non-medicinal ways in which one can get a handle on the symptoms of asthma are avoiding asthma triggers like pet dander and dust mites and monitoring asthma symptoms by way of a daily diary.
The proper asthma medication will play a key role in gaining good control of one’s asthma. As a chronic (lifelong) disease that combines inflammation of the air passageways with reoccurring episodes of mucus production, decreased airflow, and coughing. Asthma sufferers can enjoy a fulfilling and active life with a minimum of attacks, provided they are prescribed the correct medication.
Two general types of medications exist which can provide one with long-term control or quick relief of symptoms: Anti-inflammatory medications and bronchodilators.

Anti-inflammatory drugs are the most vital kind of asthma therapy for people suffering from the disease. With these medications, the asthma patient is able to attack asthma attacks on an on-going basis. Another important medication comes in the form of a steroid called corticosteroids. These anti-inflammatory drugs provide relief by reducing mucus production and swelling in the air passageways.
Bronchodilators are asthma medications made to relieve many of the asthma sufferer’s symptoms by allowing the muscle bands that tighten around the person’s air passageways during an asthma attack to relax. Once administered, bronchodilators offer rapid relief, freeing up the airways for more air to flow to and from the person’s lungs. Typically breathing will improve almost instantly for the patient. Similar to the anti-inflammatory medications, bronchodilators reduce mucus in the lungs.
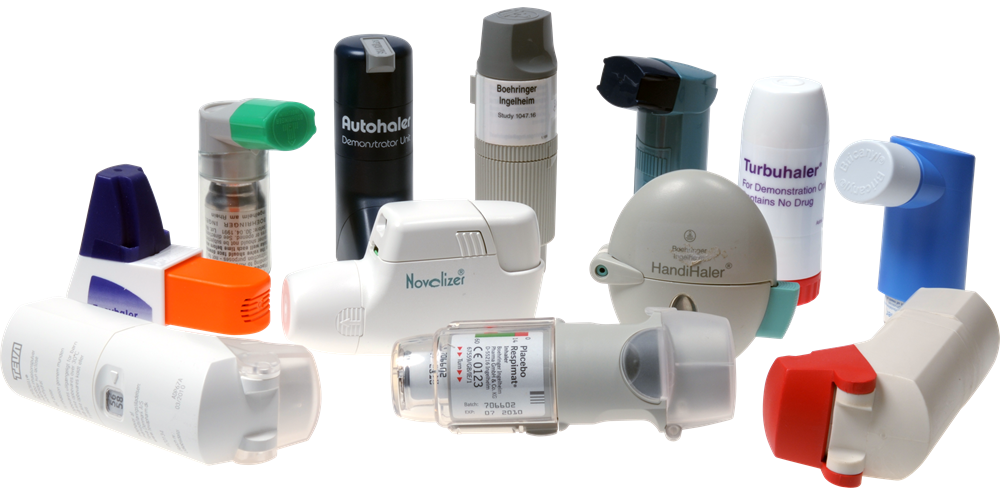
The ways in which asthma medication can be administered are through a metered dose inhaler, a dry powder inhaler, a nebulizer, or some can be taken orally, either in liquid or pill form. There is a relatively new kind of asthma drug called Xolair, which is administered by way of an injection slightly under the person’s skin.

If, for whatever reason, the asthma sufferer needs to seek an over-the-counter drug solution for his or her affliction, they are in luck. Primatene Mist and Bronkaid are the most popular or common asthma medications that do not require a physician’s prescription. These function similar to a bronchodilator in that they relax the muscles that surround the person’s airways. They can provide short-term relief, but there are some downsides to these over-the-counter remedies. Primatene Mist and Bronkaid do not prevent asthma attacks, and people who suffer from diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid disease or heart disease are cautioned not to take these medications.
Unfortunately there are a large number of asthma patients who overuse and abuse these over-the-counter medications. They are not created for use over long periods of time, but some people use them every day in order to get relief from asthma symptoms. Over-the-counter drugs for treating asthma do not actually control asthma, therefore many people taking them might not be getting correct treatment.
